Ensuring Data Protection: A Deep Dive into Cloud Security Solutions
In an increasingly digitized world, businesses and individuals rely heavily on cloud computing to store, manage, and access their data. The convenience and scalability of cloud services are undeniable, but they also come with an inherent challenge: security. The need for robust cloud security solutions is paramount to safeguard sensitive data from threats and breaches. This article delves into the realm of cloud security and explores the solutions and best practices for data protection in the cloud.
The Cloud Revolution: A Double-Edged Sword
The adoption of cloud computing has transformed the way we store and access data. Organizations no longer need to invest heavily in physical infrastructure and can instead leverage the infrastructure and services provided by cloud service providers. This shift has brought unparalleled flexibility, cost-efficiency, and scalability. However, it has also introduced new security challenges and concerns.
The shared responsibility model is a foundational concept in cloud security. It defines the division of security responsibilities between the cloud service provider (CSP) and the user. While the CSP ensures the security of the cloud infrastructure, users are responsible for securing their data and applications within the cloud. To meet these responsibilities effectively, a comprehensive approach to cloud security is necessary.
Challenges in Cloud Security
The cloud security landscape is evolving rapidly, driven by an ever-expanding threat landscape. Some of the key challenges in cloud security include:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data remains a prevalent threat. Whether through misconfiguration or malicious attacks, data breaches can have severe consequences.
- Compliance and Legal Requirements: Meeting regulatory compliance, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS, can be complex in a cloud environment, and non-compliance can result in hefty fines.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Managing user access and privileges is crucial, and poor IAM practices can lead to data exposure.
- Data Loss: Data loss can occur due to accidental deletions, hardware failures, or data corruption. Cloud data backup and recovery are essential to mitigate this risk.
- Insider Threats: Malicious or negligent actions by employees or insiders can compromise data security.
- Resource Misconfiguration: Misconfigurations in cloud resources can expose data and applications to the public internet, making them vulnerable to attack.
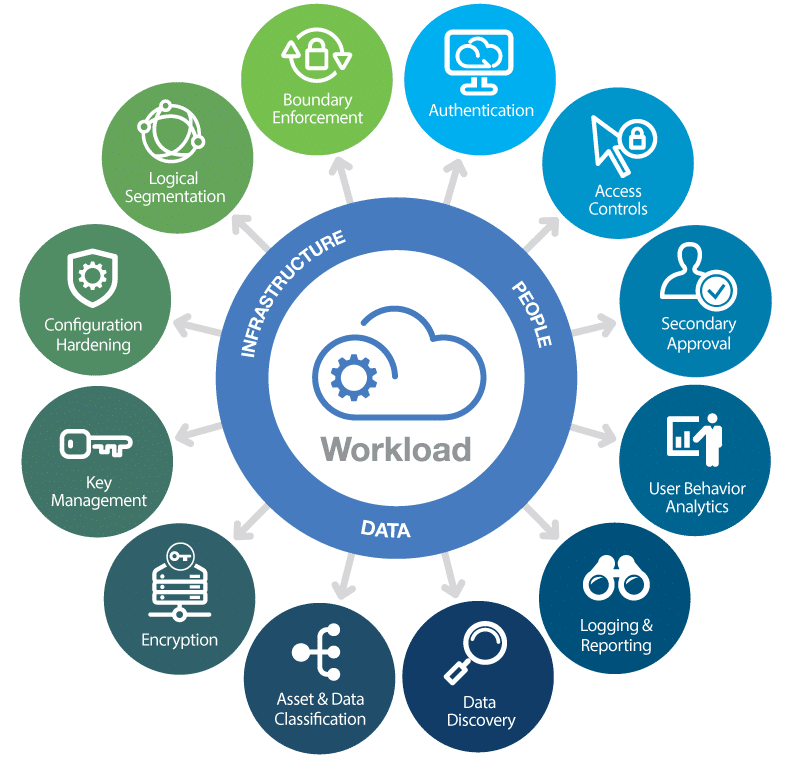
Cloud Security Solutions for Data Protection
To address these challenges and ensure data protection in the cloud, organizations and individuals can implement various cloud security solutions and best practices:
1. Encryption:
Encryption is a fundamental element of cloud data protection. It involves the transformation of data into an unreadable format that can only be accessed with the correct decryption keys. Data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest within the cloud. Many cloud providers offer encryption services, and users can also implement encryption solutions such as Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) encryption, SSL/TLS for data in transit, and server-side encryption for data at rest.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM):
Implementing strong IAM practices is essential to control and monitor access to cloud resources. This includes user authentication, authorization, and privilege management. Users should be given the least privileges required to perform their tasks, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be enforced for added security.
3. Security Groups and Network Access Controls:
Cloud security groups and network access control lists (NACLs) enable users to define rules that control inbound and outbound traffic to cloud resources. These rules help in implementing a robust network security layer to protect data.
4. Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB):
A CASB solution acts as a security gateway between an organization’s on-premises infrastructure and cloud services. It provides visibility and control over data and applications in the cloud and helps enforce security policies.
5. Data Loss Prevention (DLP):
DLP solutions enable organizations to monitor and prevent the unauthorized sharing or leakage of sensitive data. They can detect and block the transfer of sensitive information, such as credit card numbers or personal identifiers.
6. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):
SIEM systems collect and analyze log data generated throughout the organization’s technology infrastructure, including cloud services. This helps in real-time threat detection and incident response.
7. Cloud-native Security Services:
Many cloud service providers offer a range of native security services. For example, AWS provides services like AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), AWS Key Management Service (KMS), and AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF), while Azure offers Azure Security Center and Azure DDoS Protection.
8. Backup and Recovery:
Regularly backing up data in the cloud is essential for data protection. In the event of data loss or a cyberattack, having up-to-date backups ensures data can be restored.
Best Practices for Cloud Security
In addition to the specific security solutions mentioned, following best practices can significantly enhance cloud security:
1. Regular Security Audits:
Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address security weaknesses.
2. Employee Training:
Educate employees on cloud security best practices, including recognizing phishing attempts and understanding the importance of strong passwords.
3. Patch Management:
Keep cloud resources and software up to date with the latest security patches to protect against known vulnerabilities.
4. Incident Response Plan:
Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to effectively respond to security breaches.
5. Third-Party Security Assessments:
If using third-party cloud services or applications, conduct security assessments to ensure they meet your security requirements.
6. Compliance Management:
Stay up-to-date with relevant compliance requirements and implement necessary measures to comply with them.
Conclusion
As cloud computing continues to reshape the way we store and access data, the importance of cloud security cannot be overstated. Cloud security solutions, when implemented effectively, can protect sensitive data from threats, breaches, and vulnerabilities. By following best practices and leveraging the available security tools and services, individuals and organizations can harness the benefits of the cloud while maintaining robust data protection measures. As the cloud landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive in cloud security is paramount for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.